History of Temples in Garhwal
🛕 Old Temples and Early Temples
The history of temples in Garhwal is very old, with temples linked to ancient stories, such as narrative tales of deities like Shiva, Vishnu, and Devi (Goddess), and stories from the Ramayana and Mahabharata.
And some sacred sites, such as the place where the body parts of Goddess Sati fell, Shiva Linga, or other powerful sites, are historical evidence of worship and tradition.
2. Garhwal Kingdom and the Preservation of Temples
Beginning in the 9th century CE, the Garhwal Kingdom emerged as a Himalayan kingdom. After unifying several smaller principalities, rulers promoted the construction of stone and wooden temples to assert both religious and political authority.
Due to limited written records from the early period, archaeological evidence (inscriptions, iconography, temple styles) is crucial for dating these monuments.
3. Temple Construction Time
Most of Garhwal's oldest temples date back to approximately the 6th and 16th centuries CE, although repairs, renovations, and reconstructions occurred later.
The architectural style combines Nagara (North Indian) temple art and Himalayan regional techniques, designed to withstand earthquakes and snowfall.
🛕 Examples of Old, Historically Important Temples in Garhwal
Here's a look at some notable temples with ancient roots and storied historical stories:
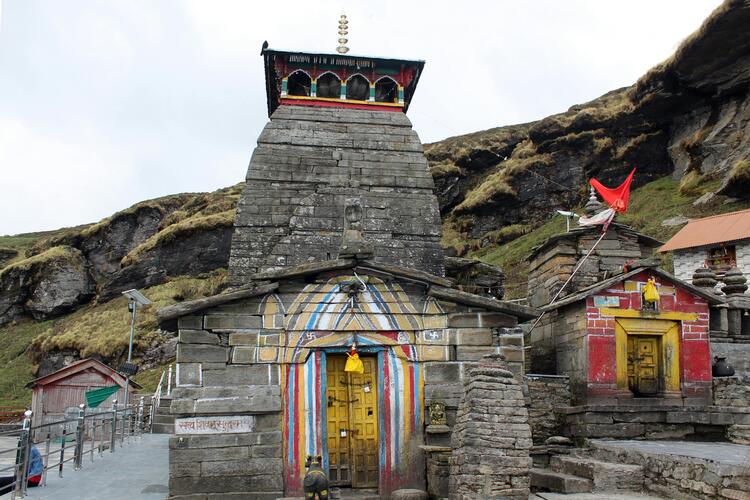
✨ Kedarnath Temple
Located high in the Garhwal Himalayas, this is one of the 12 Jyotirlingas of Shiva—one of India's holiest pilgrimage sites.
It has very ancient origins, traditionally believed to have been established by Adi Shankaracharya around the 8th century CE, although its worship probably dates back to Buddhist and early medieval times.
The temple's history is steeped in stories and devotion—connected to the Pandavas and the redemption of sins—and it has been an important religious site for centuries.
⛩️ Raghunath Temple, Devprayag
This Vishnu temple in Devprayag (Tehri Garhwal) is believed to have been built in the 8th-9th century CE, and is associated with Adi Shankaracharya and Alvar saint literature (Tamil devotional texts).
Its Dravidian architectural style and inscriptions reflect early medieval North Indian temple traditions.
🛕 Chandrabadni Devi Temple
Perched atop the Chandrakuta Range, this sacred site is associated with the Shakti Peetha tradition—sites where parts of Sati's body are believed to have fallen—and houses ancient iron tridents and idols.
⛰️ Binsar Mahadev
An ancient rock-cut temple dedicated to Shiva in a high Himalayan valley in Pauri Garhwal. It was probably built around the 9th-10th century CE and is associated with early temple styles such as the Adi Badri and Jageshwar temple groups.
Since there are no written records, folklore—which attributes the site to the Pandavas or local kings—completes its historical story.
⛩️ Surkanda Devi Temple (Tehri Garhwal)
Built around 1000 CE under the Parmar dynasty, it is a large historical temple dedicated to Devi (Goddess) with Pahari and Nagara architectural influences.
📍 Other Old Temples of Garhwal
These include the Kamleshwar Mahadev Temple in Srinagar—associated with Lord Rama and an old Shivalinga—and groups of temples like the Dewal village temple cluster, which demonstrate temple-building traditions between the 12th and 13th centuries CE.
🪔 Temple Architecture and Cultural Heritage
Regional Style: Garhwal's temples combine Nagara (North Indian) styles with local mountain methods—strong bases, stone slabs, and tiered roofs to withstand snowfall and earthquakes.
Temple Sculptures and Inscriptions: Many temples preserve rare sculptures, inscriptions, and iconography that help to historically date and contextualize them.
Continuity of Worship: Despite invasions, natural disasters, and shifting state capitals, these temples have remained living places of worship and pillars of community identity for centuries—festivals, fairs, and oral traditions persist around them.
📜 In Summary
"Old Temples of Garhwal" is not a single site, but a network of ancient sacred sites shaped by mythology, royal patronage, devotional practices, and Himalayan craftsmanship. Their history stretches back at least to the early medieval period (6th–8th century CE) to the Rajput and Garhwal Kingdom eras (16th century and later). Many temples are associated with stories of gods, sages, and epic heroes, and the physical evidence present in the temples continues to shed light on the rich spiritual and socio-political past of the Garhwal Himalayas.